A Comprehensive Guide on How to Calculate Interest on a Loan: Mastering Your Finances**
Guide or Summary:Understanding Loan InterestTypes of Loan InterestFactors Influencing Loan Interest RatesHow to Calculate Monthly PaymentsTips for Managing……
Guide or Summary:
- Understanding Loan Interest
- Types of Loan Interest
- Factors Influencing Loan Interest Rates
- How to Calculate Monthly Payments
- Tips for Managing Loan Interest
**Translation of "how to calculate interest on a loan":** 如何计算贷款利息
---
Understanding Loan Interest
When you take out a loan, whether it's for a car, a home, or personal expenses, understanding how to calculate interest on a loan is crucial. Interest is the cost of borrowing money, and it can significantly affect your total repayment amount. In this guide, we will explore the various methods to calculate loan interest, the factors that influence it, and tips to manage your loan effectively.
Types of Loan Interest
Before diving into the calculations, it's essential to understand the two main types of interest: simple interest and compound interest.
- **Simple Interest:** This is calculated only on the principal amount of the loan. The formula is straightforward:
\[
\text{Simple Interest} = \text{Principal} \times \text{Rate} \times \text{Time}
\]
For example, if you borrow $1,000 at an interest rate of 5% for 3 years, the interest would be:
1000 \times 0.05 \times 3 = 150
- **Compound Interest:** This is calculated on the principal amount and also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. The formula for compound interest is:
A = P \left(1 + \frac{r}{n}\right)^{nt}
where:
- \( A \) is the amount of money accumulated after n years, including interest.
- \( P \) is the principal amount (the initial amount of money).
- \( r \) is the annual interest rate (decimal).
- \( n \) is the number of times that interest is compounded per year.
- \( t \) is the time the money is invested or borrowed for, in years.
For instance, if you take a loan of $1,000 at a 5% annual interest rate compounded annually for 3 years, the calculation would be:
\[
A = 1000 \left(1 + \frac{0.05}{1}\right)^{1 \times 3} = 1000 \times (1.05)^3 \approx 1157.63
\]
Thus, the total interest paid would be approximately $157.63.

Factors Influencing Loan Interest Rates
Several factors can influence the interest rates you receive on a loan:
- **Credit Score:** Lenders use your credit score to determine your creditworthiness. A higher score typically results in lower interest rates.
- **Loan Amount and Term:** Larger loans or longer repayment terms may have different interest rates. Generally, shorter-term loans have lower rates.
- **Market Conditions:** Economic factors, such as inflation and the central bank's interest rates, can also affect loan interest rates.
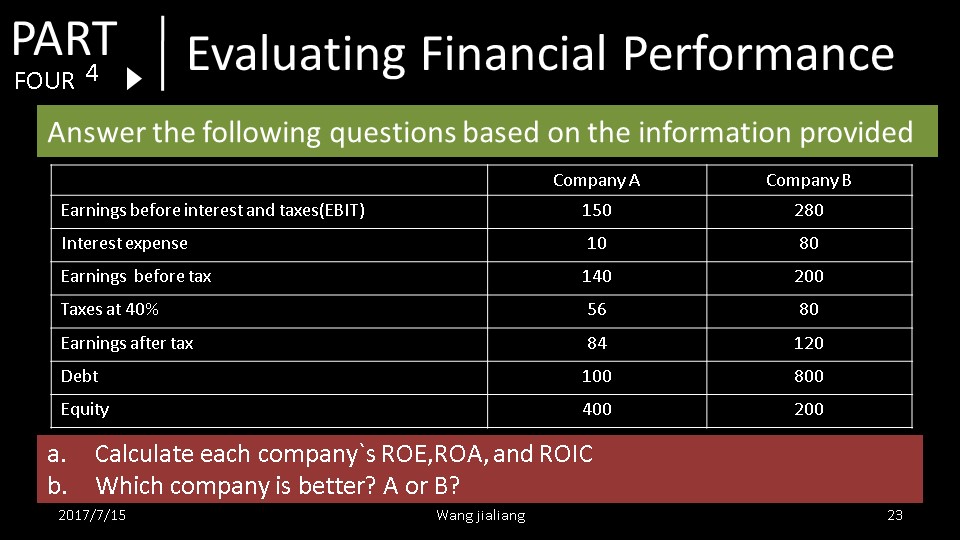
How to Calculate Monthly Payments
Once you understand how to calculate interest on a loan, you may want to determine your monthly payments. The formula for calculating monthly payments on an amortizing loan is:
M = P \frac{r(1 + r)^n}{(1 + r)^n - 1}
where:
- \( M \) is the total monthly payment.
- \( P \) is the principal loan amount.
- \( r \) is the monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12).
- \( n \) is the number of payments (loan term in months).
For example, for a $10,000 loan at a 5% annual interest rate over 5 years:
- Monthly interest rate \( r = \frac{0.05}{12} \approx 0.004167 \)
- Total number of payments \( n = 5 \times 12 = 60 \)
Plugging these values into the formula gives you a monthly payment of approximately $188.71.
Tips for Managing Loan Interest
1. **Shop Around:** Different lenders offer varying interest rates. Always compare options before committing.
2. **Consider Refinancing:** If interest rates drop or your credit score improves, refinancing could save you money.
3. **Make Extra Payments:** Paying more than the minimum can reduce the principal faster and save on interest.
By mastering how to calculate interest on a loan, you can make informed financial decisions and manage your loans effectively. Understanding the implications of interest rates and payment structures will empower you to take control of your financial future.