Understanding the Differences Between Subsidized and Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
Guide or Summary:Subsidized federal Stafford loans are need-based loans offered to undergraduate students to help cover the cost of higher education. The ke……
Guide or Summary:
When it comes to financing your education, understanding the types of loans available is crucial. Among the most common options are subsidized and unsubsidized federal Stafford loans. These loans are designed to help students cover the costs of college, but they come with different terms and conditions that can significantly impact your financial future. In this article, we will explore the key differences between subsidized and unsubsidized federal Stafford loans, helping you make an informed decision about which option is best for you.
### What Are Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans?
Subsidized federal Stafford loans are need-based loans offered to undergraduate students to help cover the cost of higher education. The key feature of these loans is that the federal government pays the interest while you are in school at least half-time, during the grace period after graduation, and during any periods of deferment. This means that the amount you owe when you graduate will be less than what you would owe with an unsubsidized loan, making it a more affordable option for those who qualify.
To be eligible for subsidized federal Stafford loans, you must demonstrate financial need, which is determined by your FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) application. The amount you can borrow is capped based on your year in school and your financial need, which is assessed each academic year.
### What Are Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans?
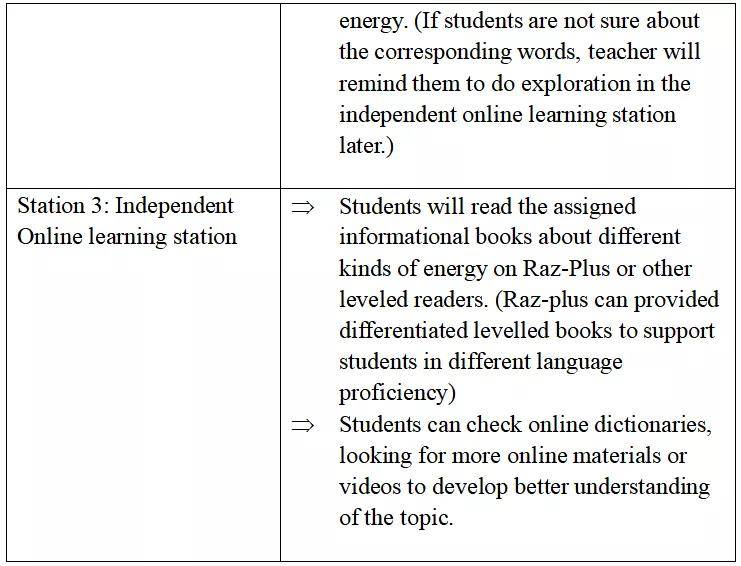
On the other hand, unsubsidized federal Stafford loans are available to both undergraduate and graduate students, regardless of financial need. Unlike subsidized loans, the borrower is responsible for paying the interest on these loans from the moment the funds are disbursed. This means that if you choose not to make interest payments while in school, the interest will accrue and be added to your principal balance, increasing the total amount you will owe upon graduation.
The borrowing limits for unsubsidized federal Stafford loans are generally higher than for subsidized loans, providing more financial flexibility for students. However, because you are responsible for all the interest, it is essential to consider your future financial situation when deciding how much to borrow.
### Key Differences Between Subsidized and Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans
1. **Interest Payments**: The most significant difference between subsidized and unsubsidized federal Stafford loans is who pays the interest. With subsidized loans, the government covers the interest while you are in school, while with unsubsidized loans, you are responsible for all interest payments.
2. **Financial Need**: Subsidized federal Stafford loans are awarded based on financial need, whereas unsubsidized federal Stafford loans are available to all eligible students regardless of their financial situation.
3. **Borrowing Limits**: The maximum amount you can borrow differs between the two types of loans. Unsubsidized federal Stafford loans usually have higher borrowing limits, making them a viable option for students who need additional funds.
4. **Eligibility**: Only undergraduate students can receive subsidized federal Stafford loans, while both undergraduate and graduate students can apply for unsubsidized federal Stafford loans.
### Conclusion

Choosing between subsidized and unsubsidized federal Stafford loans can significantly affect your financial situation after graduation. If you qualify for need-based assistance, subsidized loans can save you money in the long run. However, if you do not qualify, unsubsidized loans still provide an essential resource to help fund your education. It is vital to carefully evaluate your financial needs, future earning potential, and loan repayment options before making a decision. By understanding the differences between these two types of loans, you can better navigate the complexities of student financing and make choices that will support your academic and financial goals.